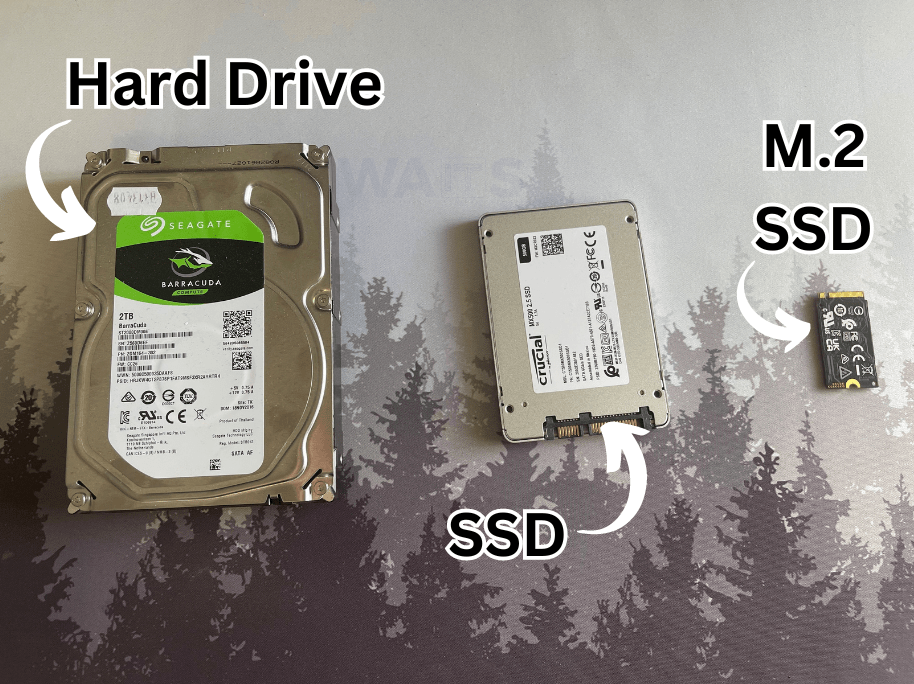
With tax time sales rapidly approaching, many people tend to rush out and buy a new laptop or computer. However, when choosing a new laptop or computer, many people tend to gloss over the specifications of the machine – with data storage being a big component missed. Within the confusing world of data storage, there are several options available – each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The three commonly used types of drives are Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Solid State Drive (SSD), and M.2 drives (PCIe NVMe variants). Understanding the differences between these drives is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to a storage solution for your devices.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
A HDD, whether internal or external, serves as a vital repository for various forms of data, including applications, files, and the operating system. Known for their non-volatile nature, HDDs retain stored data even in the absence of power. These drives operate through two primary components: a spinning “platter” and an actuator arm.
The platter, a circular magnetic disk, comprises of tracks and sectors where data is stored, while the actuator arm moves across the platter to facilitate data reading and writing. As the platter spins on a spindle, the actuator arm’s movement accelerates the read and write processes. This mechanism is often audible in external HDDs when data is accessed. While external HDDs excel in long-term storage, they are not recommended for use as primary storage in computers or laptops as they are quite bulky and can take a long time to load.
Pros
- Quite affordable compared to other storage devices
- Readily available on the market
- Larger storage base capacity
- Non-volatile memory
Cons
- They are quite slow
- Generally have a shorter lifespan
- Their size is inconvenient
- Magnets can wipe their storage
SSD (Solid State Drive)
SSDs are a prevalent type of storage device found in modern computers. Over time, SSDs have gradually overtaken the traditional hard drives in computer systems due to their speed advantages. Unlike hard drives, SSDs rely on solid-state flash memory rather than mechanical moving parts to store and retrieve data. Because there is no moving components, this contributes to their enhanced durability, leading to a longer lifespan compared to hard drives. The benefits of SSDs extend beyond longevity; they offer significantly faster performance, resulting in quicker boot times for operating systems, quicker loading of programs, and quicker file-saving processes.
Pros
- No moving parts
- Typically smaller and lighter than HDDs
- Offers faster data transfer rates
- Quicker boot times and application loading
Cons
- Pricier than HDDs
- More limited storage capacity
- Potential data loss if the drive fails
- Limited write codes, meaning frequent, heavy use can degrade their performance over time
M.2 Drive
The M.2 drive, specifically the PCIe NVMe variants, is a form factor SSD – it’s the newer and smaller form factor than previous SSDs. This drive is roughly the size of a stick of chewing gum – it’s small and slim size makes it ideal for computers that are lightweight and portable, like laptops or notebooks. Between the basic SSD and the M.2, they differ in storage technology. M.2 drives communicate directly with the system CPU using the PCIe sockets which are placed directly on the motherboard.
Pros
- Form factor SSD
- Connects directly to the motherboard
- Exceptionally fast read and write speeds
- Low power consumption
Cons
- Can be quite expensive
- Not all motherboards have a M.2 drive slot
- They generate heat more
- Limited capacity compared to others
In conclusion, the choice between HDDs, SSDs, and M.2 drives depends on various factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and physical space limitations. HDDs remain a cost-effective solution for high-capacity storage needs, while SSDs offer superior performance with faster data access times. M.2 drives, specifically PCIe NVMe variants, represent the cutting edge of storage technology, providing unparalleled speed and efficiency for demanding applications. By understanding the differences between these drives, you can select the most suitable option to meet your needs.